Augmented reality is a technology and a tool that displays and creates an enhanced view of physical reality by immersing digital elements such as images, text, sounds, and videos. Also, the augmented reality software (ARKit for iOS devices or ARCore for Android) is able to understand its physical environment to detect flat surfaces, movements, and the position of the phone in relation to its surroundings.
The application of augmented reality in digital content display comes with benefits that will continue to increase productivity, reduce travel time, speed up training and more. It takes the name “augmented reality” because the virtual elements increase the quality of the real experience.
If you want to know more about the benefits of augmented reality, this article is for you!
What is Reality Technology?
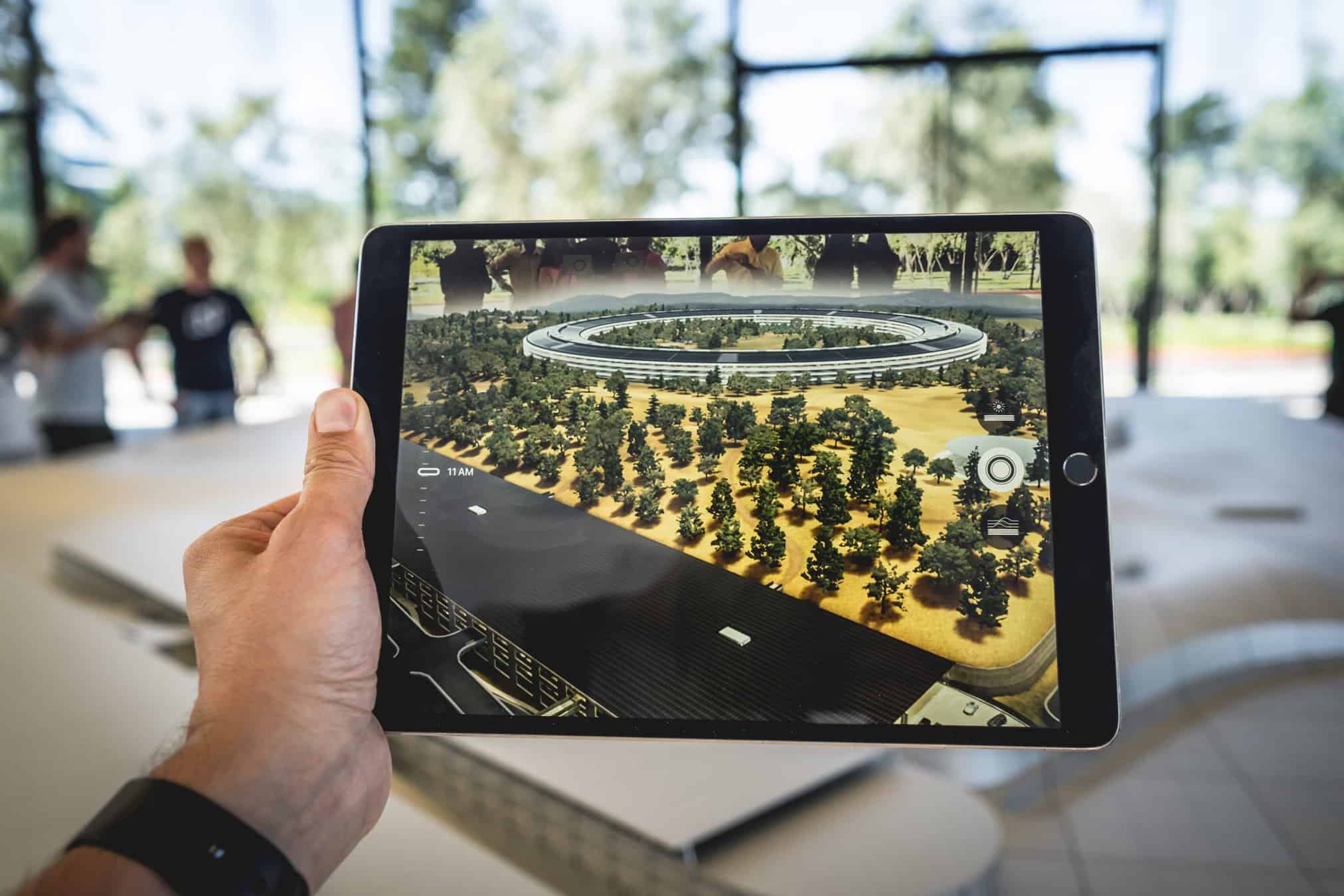
Reality Technology is a general term used to describe a group of reality-creating technologies, including augmented reality, mixed reality, virtual reality, 360-degree video, and other cutting-edge immersive technologies, all of which can use computer-generated content to completely artificially create virtual environments. You can visualize those virtual images and 3D objects on your AR-enabled device (modern phones only).
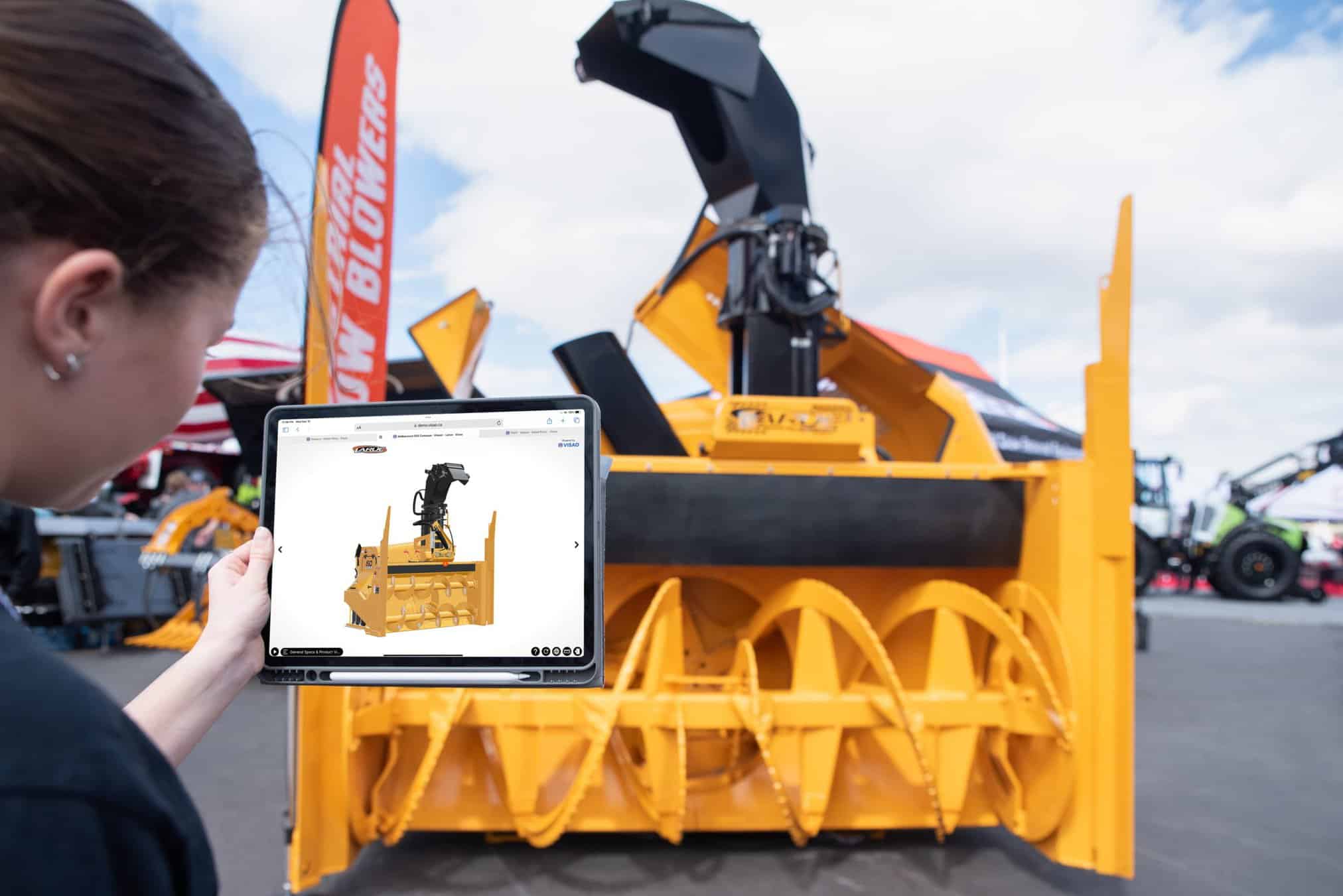
Here is a representation of a product in augmented reality taken with a mobile device:

How does augmented reality (AR) work?
Augmented reality display technology uses a combination of sensors and software features. In addition to the software, compatible AR devices have a combination of sensors, including depth tracking ( to measure depth level), an accelerometer ( to track changes in movement) and a gyroscope ( to track the orientation of the device). These sensors allow an accurate and dynamic presentation of the 3D model in the physical environment. When the AR tool is activated, both the software and internal sensors are enabled and allow the visualization of 3D models directly in the physical field of view of a device‘s camera.
The key to this reality feature is the mix between the real and virtual worlds, real-time interaction, and accurate 3D registration of virtual and real objects.To use this reality technology, you need a camera-equipped device, such as a smartphone, tablet or smart glasses, as well as AR software. iOs devices that support ARKit (its integrated AR software) must be equipped with the A9 chip or newer, which means iPhone 6s and above. Android devices that support ARCore include Android 8.0 or later, to see the full list, click here.
When a user is pointing their device and looking at a real object, the augmented reality software is able to understand its physical environment to detect flat surfaces, movement, and the position of the phone in relation to its surroundings using computer vision technology (which studies the video stream). Other augmented reality features include: SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping), depth tracking (data from a sensor calculates the distance of objects), object recognition (collects data about user interactions and sends it for processing).

In addition to the software, compatible AR devices have a combination of sensors, including depth tracking ( to measure depth level), an accelerometer ( to track changes in movement) and a gyroscope ( to track the orientation of the device). These sensors allow an accurate and dynamic presentation of the three-dimensional objects in the physical environment. Together, both the software and internal sensors are enabled and allow the visualization of 3D models directly in the physical field of view of a device’s camera.
Finally, the device then saves information about the object from the cloud, similar to the way that a web browser loads a page via a URL. However, an important difference is that the AR information is illustrated in a 3-D “experience” overlaying a digital image on the virtual object rather than in a 2-D page on a screen.
The understanding of what the user sees is therefore partly real, as in the case of physical objects, and partly digital, in a physical environment.
For concrete use cases from companies using augmented reality, click here
Where and why do we use Augmented Reality ?
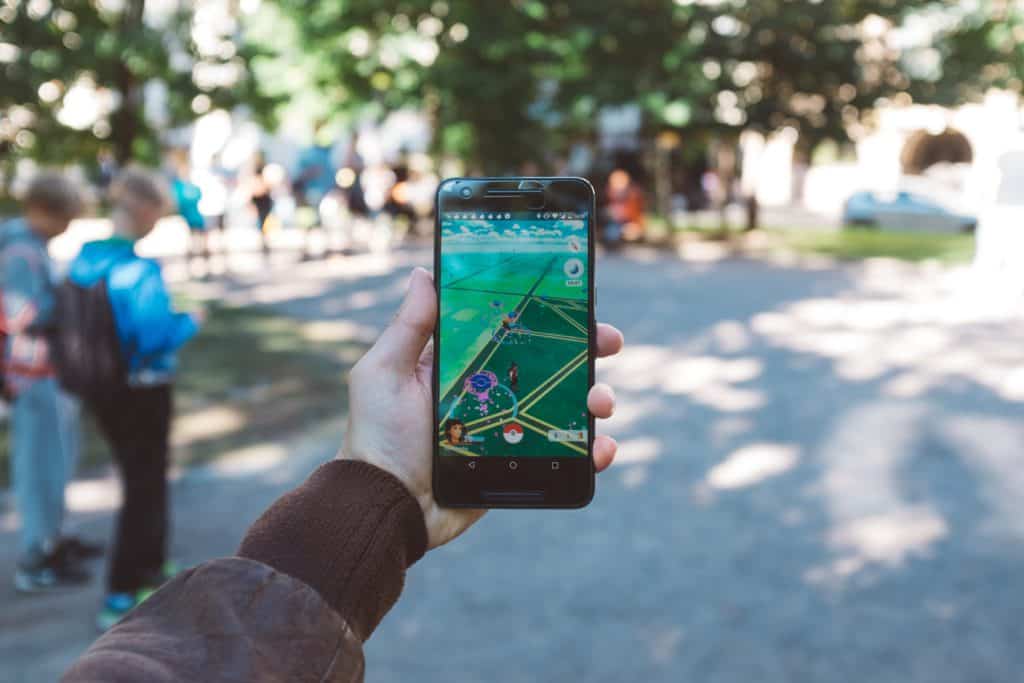
Augmented reality is currently being used in many industries such as education, healthcare (medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention) , real estate and gaming (think Pokémon GO), and its uses are endless. Here are some useful use cases for this digital content.
Here is an example of how augmented reality is used through a mobile video game called Pokemon Go:

Increase productivity level
Productivity gains go far beyond manufacturing. One of the main use cases for AR is customer support. Many are planning to integrate AR into customer support, and the value is clear.
For example, AR makes a help desk much more efficient. Customer service agents can see what the customer sees, also known as see-what-I-see (SWIS). AR technology as in its name, indicates that it augments and enriches our physical environment with virtual information not perceptible to the naked eye, whether in the form of images or text, and this in real time.
Moreover, it is possible to examine the problem with their own eyes and have access to the information bank at any time. They can also use the digital overlay to guide the customer through the repair or configuration process. This increases productivity by reducing call times. AR allows service agents to handle more customers. It also reduces wait times and increases first call resolution rates.
For this reason, increased employee productivity has been cited as a major benefit that surpasses traditional learning measures.

Remote expert assistance
Augmented reality allows professionals to be in multiple locations or physical space at once. When a field technician is repairing equipment in a remote area and gets stuck, he or she can use an enterprise augmented reality (AR) solution to immediately connect to a subject matter expert (SME). This subject matter expert can be anywhere, at home, at work or even abroad, using a wearable device, such as a cell phone in most cases, or a wearable device.
This not only allows the expert to see what the technician is looking at, but also to reach the target directly with instructions, making the customer experience very efficient. For example, instead of trying to indicate which screw needs to be removed, he can simply draw a circle over it.
Augmented reality especially plays an important role for complex innovations, as it allows the customer experience to be about the product in their own surroundings- and not just on a screen- at a realistic 1:1 size for space planning. For example, augmented reality provides the ability to visualize the configuration and location of machines, without having to bring the equipment onsite. All you would need would be handheld devices such as mobile phones or wearable device.
Here is an example from the Fabtech Trade show that showcases how convenient, time and money saving augmented reality can be. You can easily see how the object will fit into the space and field of view in which you plan to install it. This makes it easy to draw floor plans to scale or visualize new equipment with a mobile device. That being said, this tool ensures that everything fits perfectly in the physical space of choice and makes planning much easier.

E-commerce
According to a study by EcomDash, 45% of online shoppers believe that augmented reality (AR) saves time on their decision making. This means that AR is more likely to engage prospects than a PowerPoint and videos. Why? Augmented reality plays an important role for complex innovations, as it allows customers to experience the product in their own surroundings- and not just on a screen- at a realistic 1:1 size for space planning. This makes it easy to draw floor plans to scale or visualize new equipment with a mobile device. This tool ensures that everything fits perfectly and makes planning much easier.
As a result, your prospects will remember your items much more, particularly if your competitors don’t offer this option, and they’ll be much more likely to contact your sales team afterwards ( increase your conversion rate!). That being said, their validation purpose will be more clear.
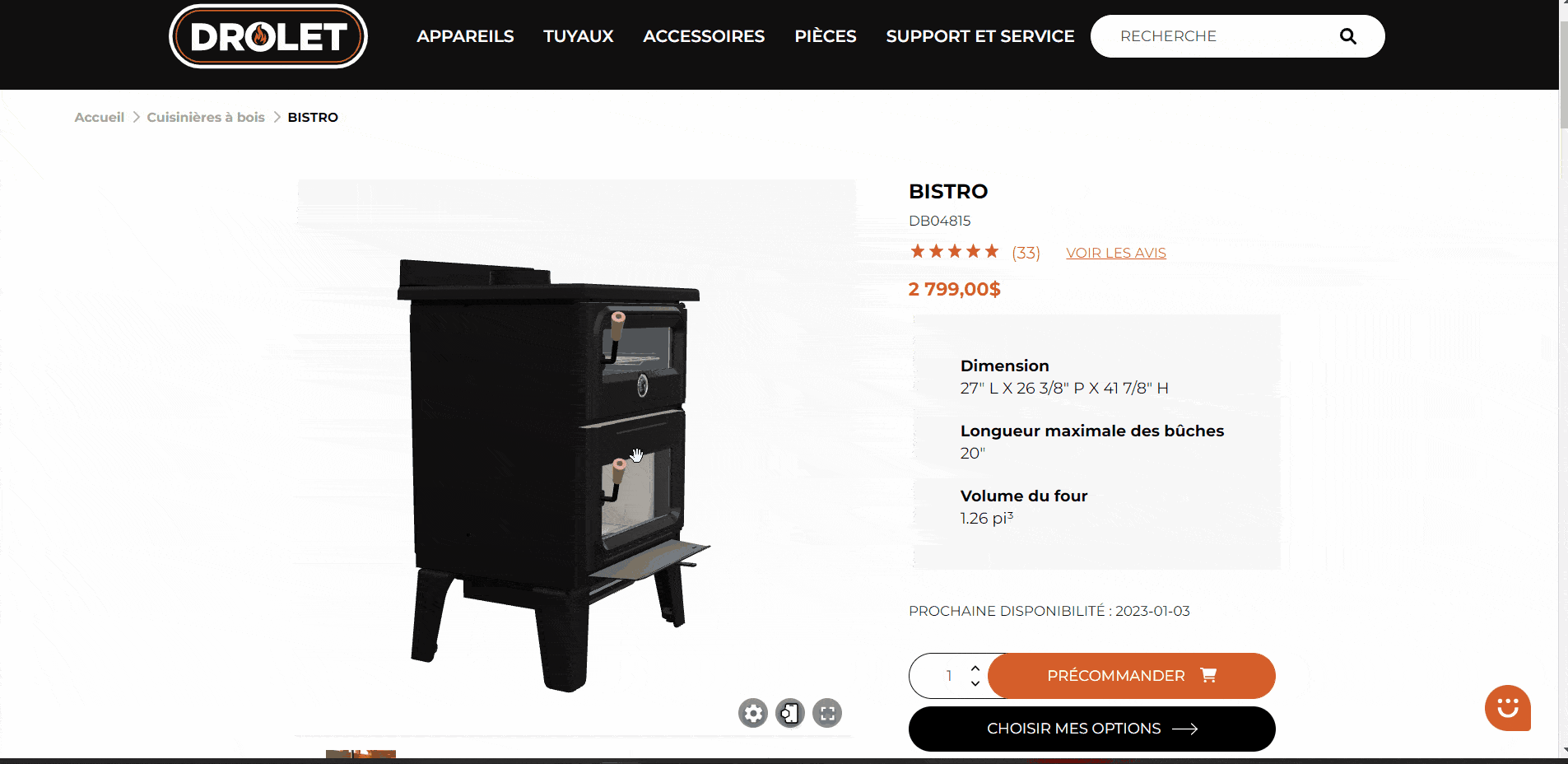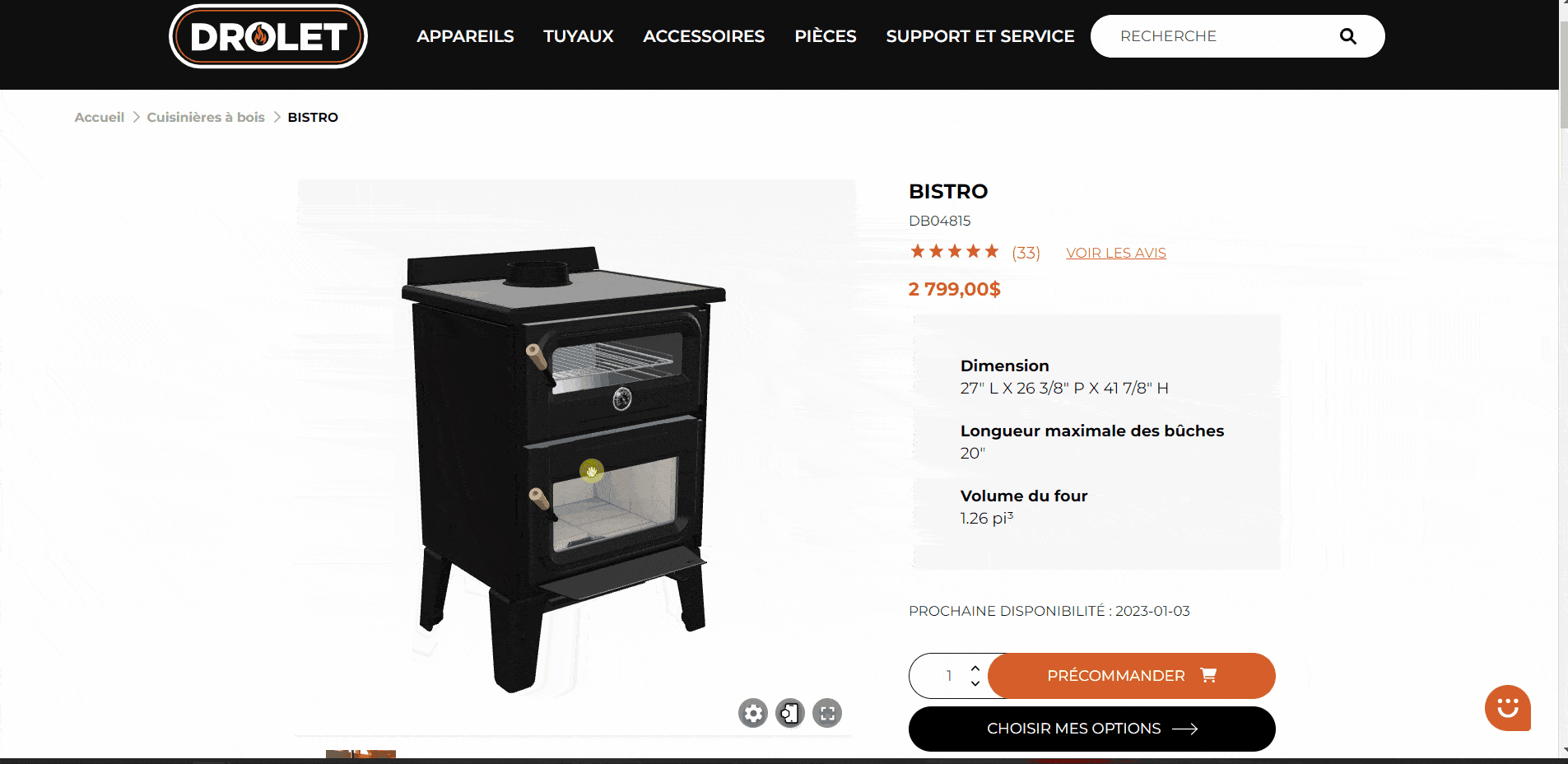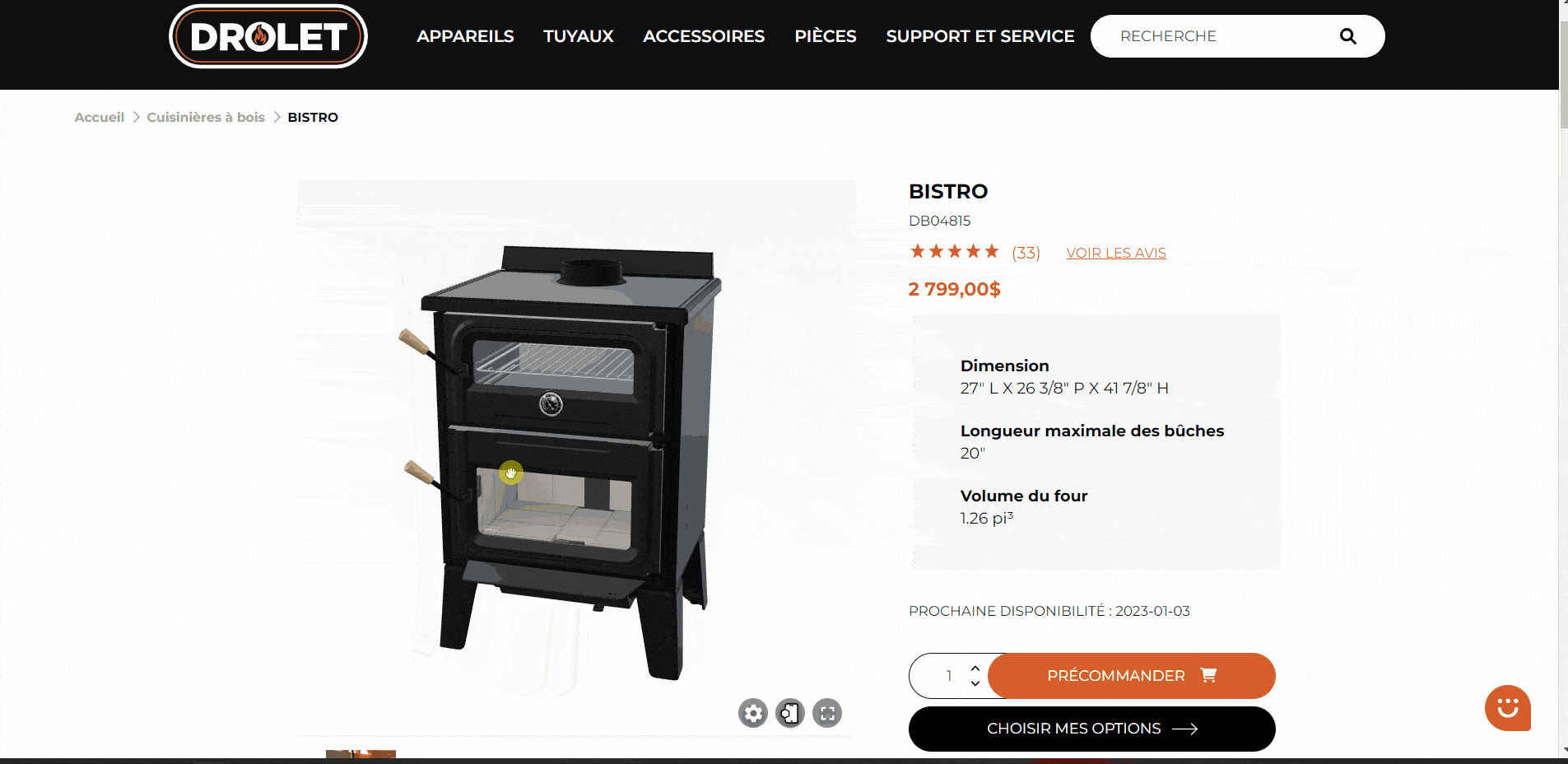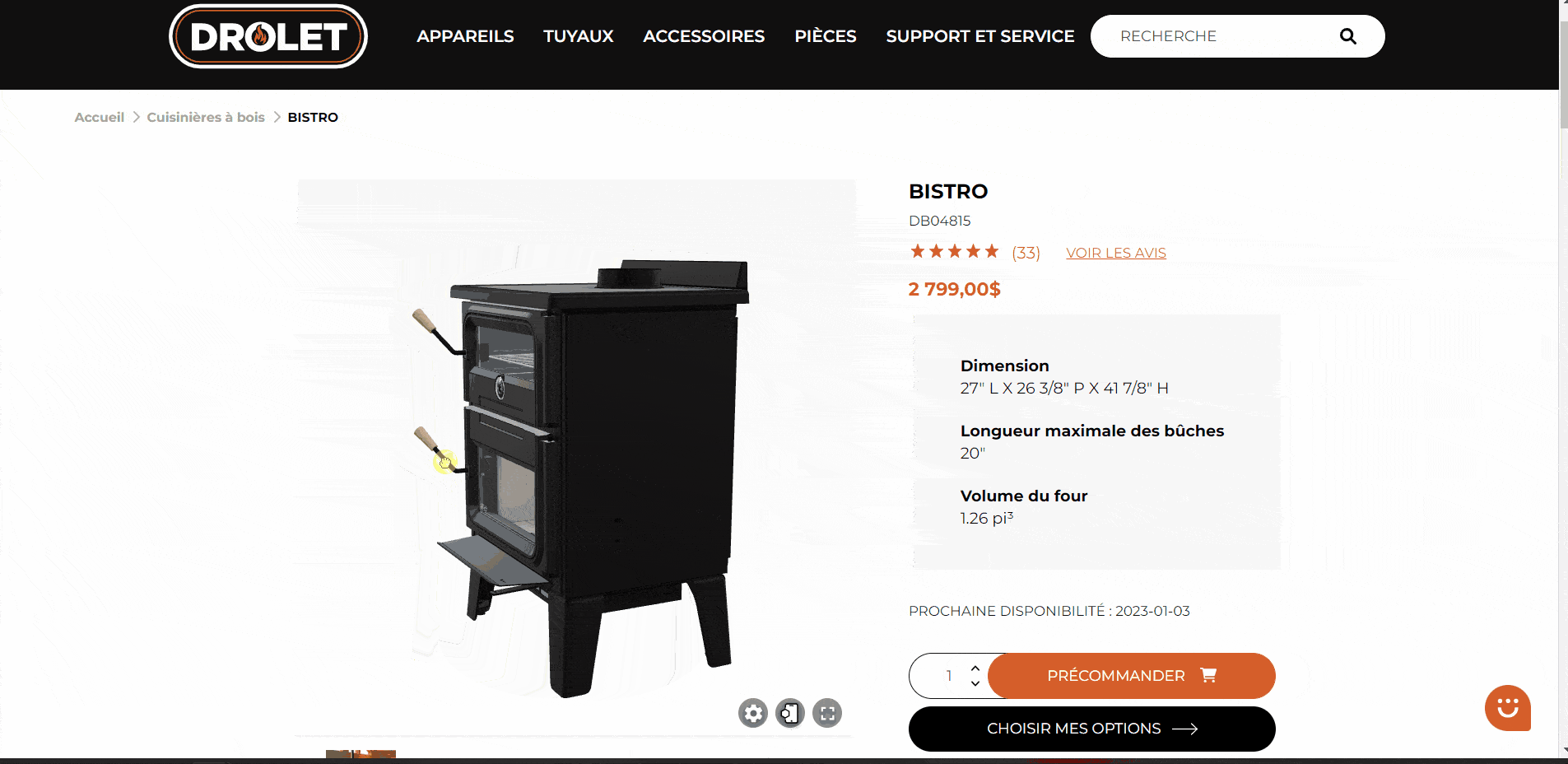
Here is an article on what you can do to accelerate your sales through 3D visualization and AR
Remote and in-person selling
Augmented reality applications also provide marketing teams with a valuable new tool to add to their tool belts. Whether it’s in a B2B or B2C context, being able to actually show a customer a product they can visualize in their space or interact with is a big advantage. This lets customers visualize how different item models and see how they would look and work in their home environment. AR makes it easier, more affordable, and more convenient for customers to view prototypes from the comfort of their home!

Education and learning processes
Productivity gains reach well beyond manufacturing. One major use case is AR for customer support. More and more people are planning on incorporating AR into technical support and interactive user manuals for customers, and the value here is clear.
This technology lets organizations train employees from anywhere with user interaction. AR lets operators gain experience on machinery, and equipment in a completely risk-free environment. Science Direct’s statistics show that AR is also proven to create higher retention rates than traditional methods by encouraging customer engagement.
Everyone is aware that experience makes for the finest teacher, which explains why AR is so successful. Students have a far better understanding of the processes by imitating real-world scenarios. The use of simulations is preferable than only reading about, viewing, or hearing about them. In other words, AR is soon becoming part of everyday life.
What is the difference between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality?
With AR, 3D digital elements are integrated into a physical field of vision. This technology can be used with AR compatible mobile devices. With virtual reality, these elements are integrated into a completely virtual environment. VR completely removes your field of vision and can only be achieved with VR headsets, glasses and goggles.
With augmented reality (AR), your surroundings are enhanced by the addition of digital features, frequently used with a smartphone’s camera. Basically, through the use of digital visual 3D components, sound, or other sensory inputs, augmented reality creates an enhanced version of the real physical environment.
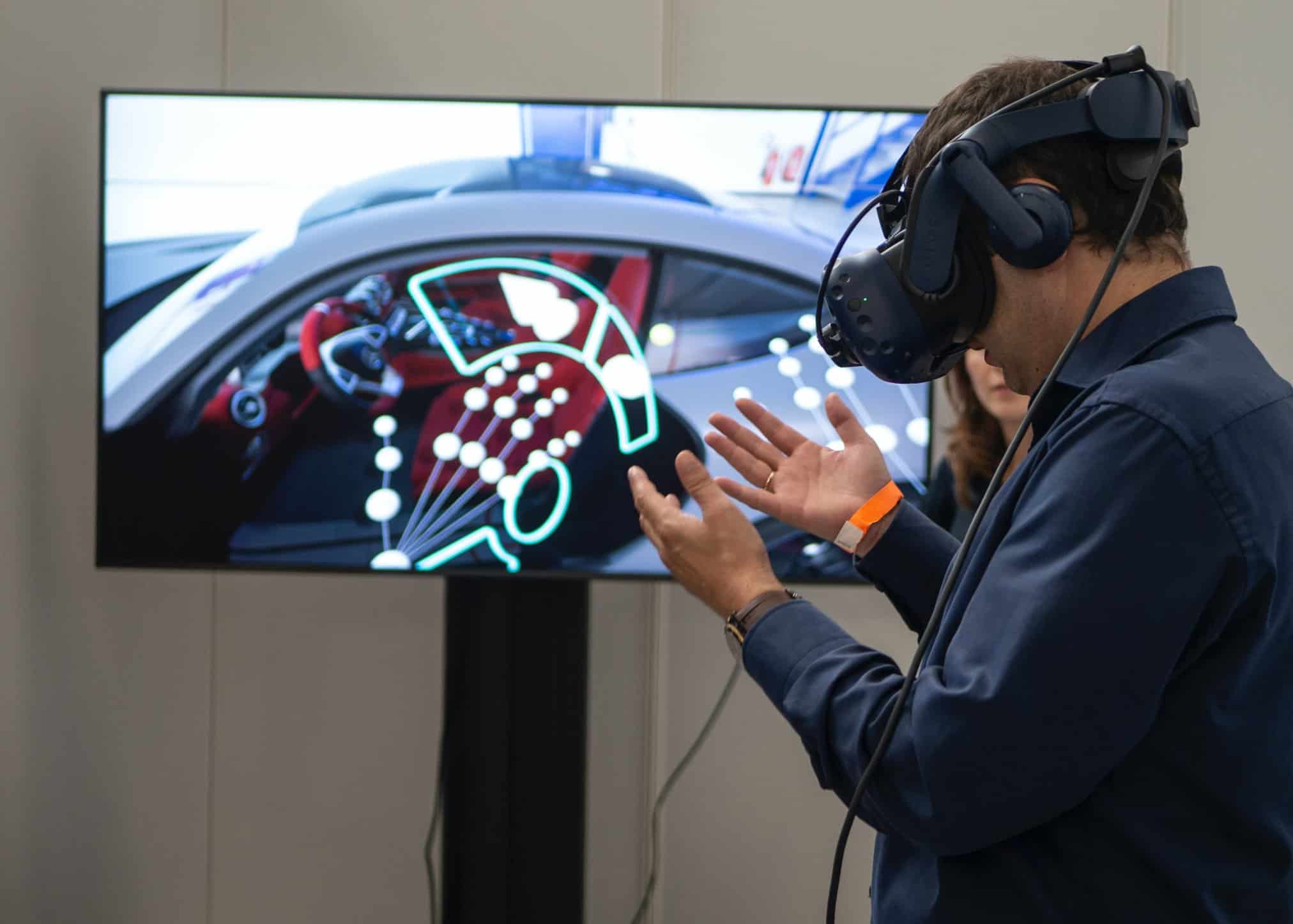
On the other hand, virtual reality (VR) is a immersive experience that substitute a real-life environment or a real-world environment and real-world objects with a simulated one. In fact, virtual reality is an artificial environment representing a 3D space that is created with software and presented to the user in such a way that the user suspends belief and accepts it as a real environment. This technology can only be realized with VR headsets (like Oculus), glasses (Google Glass) and goggles. Two of the five senses are the most used to experience virtual reality: sight and sound.
Here is an example of what a virtual reality headset looks like:

What are the advantages of using AR?
To summarize it all, here are the major advantages of using AR:
One advantage is that if the user moves, the size and orientation of the AR display will immediately adapt to the change in context. Similarly, users in different positions, for example in an industrial environment, can look at the same object but be presented with different AR experiences, tailored to their needs. These images representing virtual objects or virtual content can be tailored specifically to a chosen space emulating real environments. Customers can then validate whether the object is suitable for them or not. After testing the user-friendly augmented reality device via their phone, consumers now have a clearer vision of what they might buy, making their decision easier and faster. Overall, augmented reality reassures the customer and gives them more confidence when making a decision, resulting in high conversion rates. In addition, the use of augmented reality improves the perception of reality, making the consumer more likely to have a better and faster validation goal.

How can Visao’s experts help you?
Visao provides a web-based platform that allows manufacturers to use their CAD files to create interactive 3D virtual content of their products for marketing, sales processes, trade shows and production, the perfect tool for business users. We also provide services to accompany you in the process of creating your own augmented reality tools.
Ready to create your own 3D visual content? Request a live demonstration of Visao’s 3D and augmented reality solutions.

